Structure: Industrial Plant Design Key Features Problems
Industrial plant structure design is not an easy task; it requires a meticulous and integrated approach to ensure that such structures are functional, safe, and efficient. Industrial structures need to be designed to resist heavy loads, dynamic loads, and even extreme weather conditions. In this blog, we will examine the key components of industrial plant structure design that make it a crucial part of the engineering process.
1.Importance of Industrial Plant Structure Design
Industrial plant buildings are the pillars of most manufacturing, power generation, and processing plants. The structure’s design does influence efficiency, safety, and sustainability in the long run. Load-carrying capacity, seismic behavior, and material strength are some of the factors that engineers need to consider to make such buildings withstanding the test of time. It can lead to efficient operations and a more secure working environment in a properly designed industrial plant.
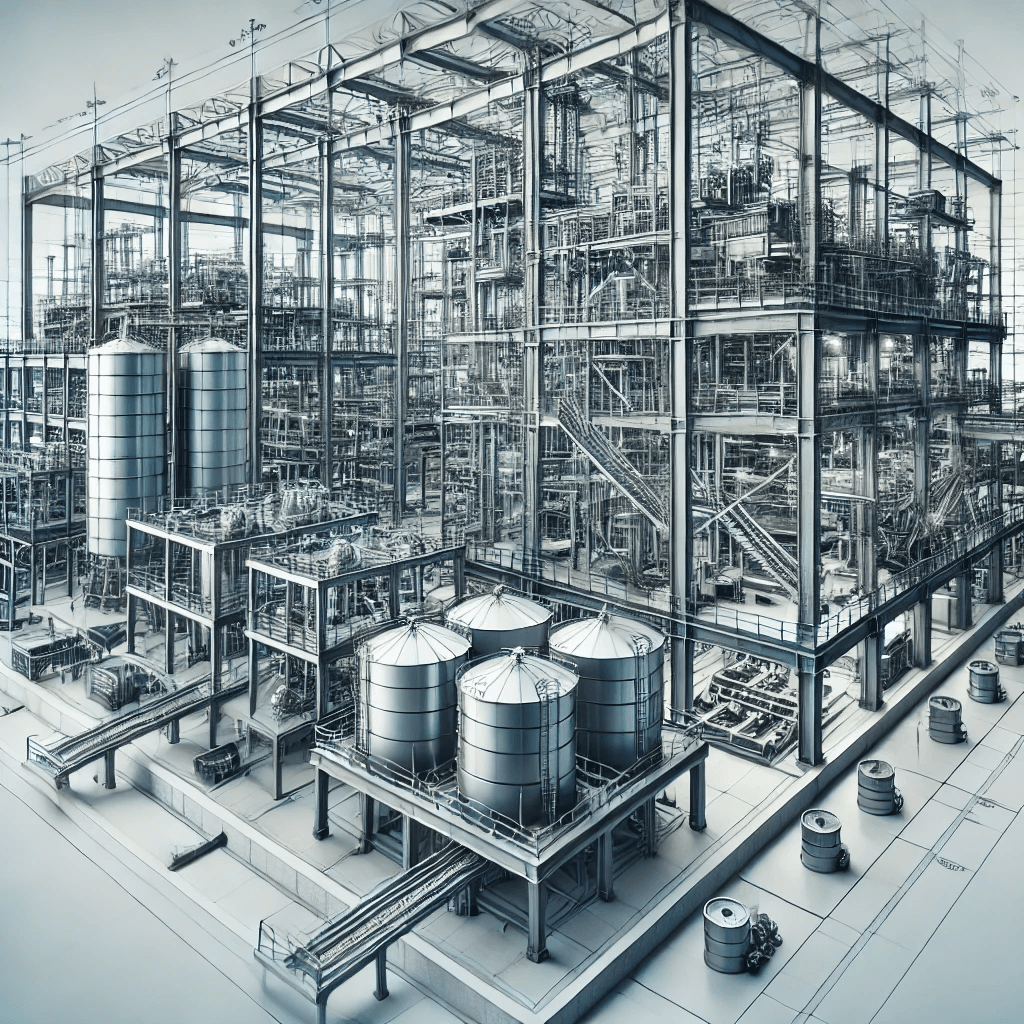
2.Key Structural Components in Industrial Plants
An industrial factory comprises a series of primary structural components, including steel frames, support columns, foundations, and roof trusses. These components are all tasked with maintaining the stability of the overall structure. Material selection is also important; reinforced concrete and high-strength steel are usually used to provide resistance to mechanical and environmental loads. With the selection of these components through a judicious choice and designing them with great care, engineers can provide a firm and robust foundation for industrial processes.
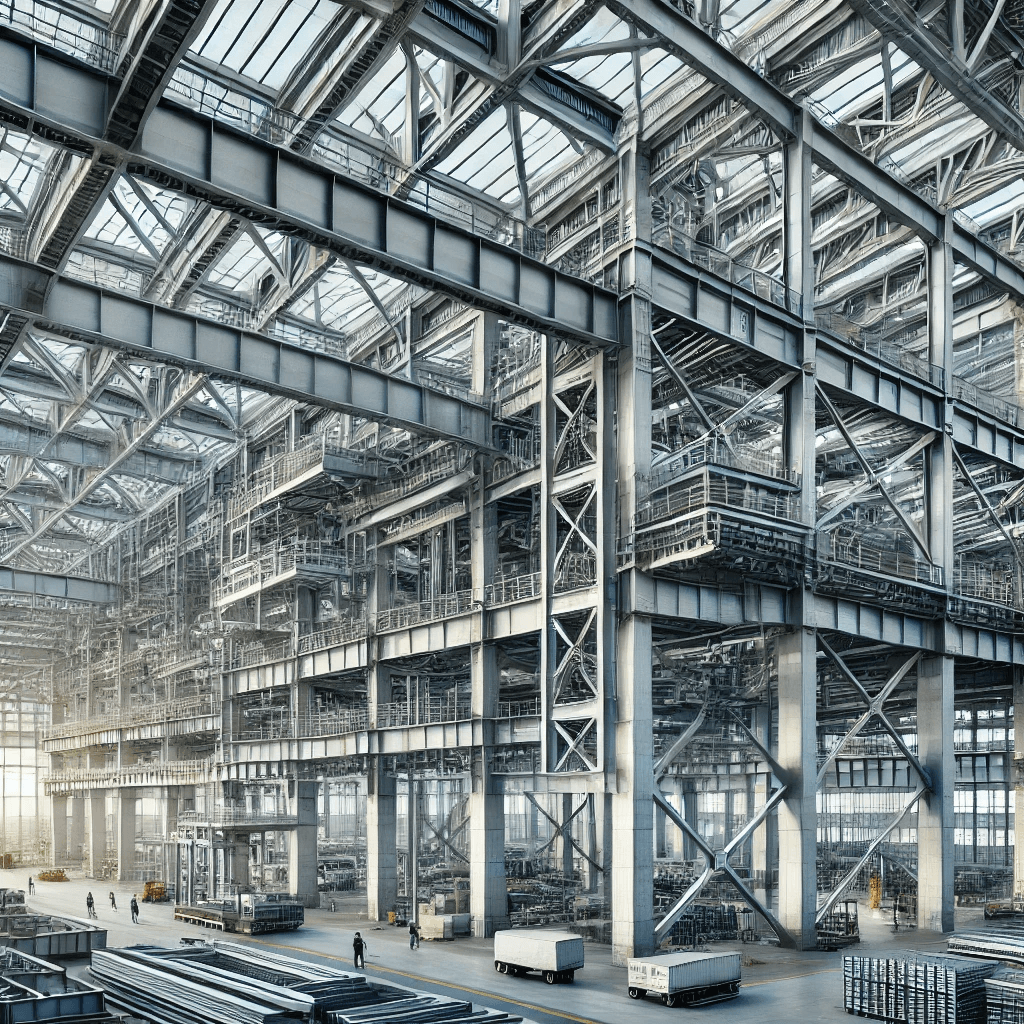
3.Factors Affecting Structural Design
Structural design is regulated by various factors. Geographical location, climatic conditions, and seismology are all considerations for the design of an industrial plant. Engineers need to consider numerous factors, including wind loads, temperature variations, and soil composition, to be able to design the plant to achieve maximum stability and longevity. By considering all these factors, they are able to design structures that are functional as well as resistant to stresses in their surroundings.
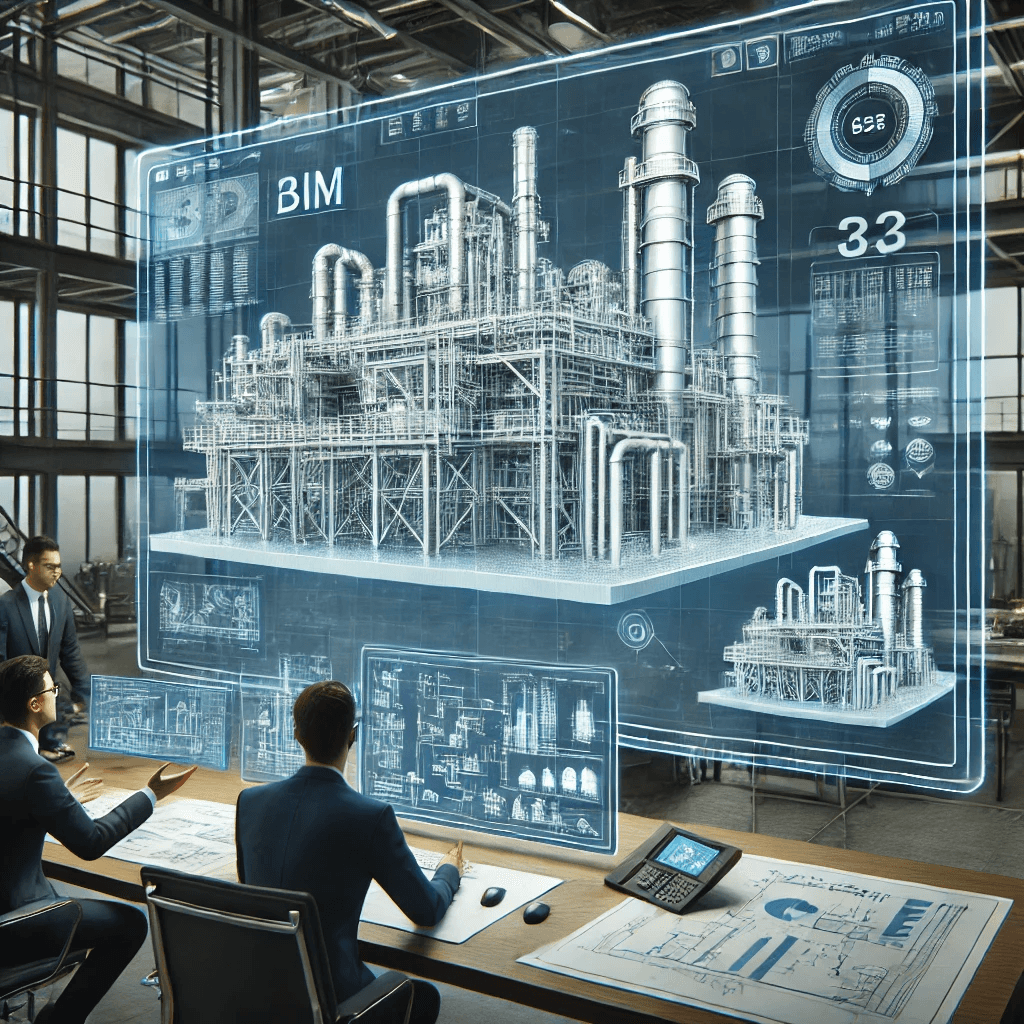
4.Role of Technology in Industrial Plant Design
The technology revolution has altered the design theme of industrial plants. With the strong capabilities of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 3D structural analysis, engineers are able to come up with precise models with early warning of oncoming design failure. Virtual simulations that can be prepared in advance are most likely to forecast the behavior of a structure under various conditions. This enhances the efficiency of the project and decreases the risk of expensive error-making. In addition to improvement in accuracy, the application of technology in design results in successful collaboration among design teams.
5.Safety and Compliance in Structural Design
Safety is paramount when designing industrial plant buildings. Engineers are required to comply with local and international safety standards, including OSHA and ISO requirements. These include fire-resistance, emergency exit, and structural support against hazards. Designing for safety will allow engineers to develop conditions that safeguard workers and reduce risks.

6.Future Trends in Industrial Plant Structure Design
The industrial plant design future is bright. We can expect more emphasis on sustainable building materials, modularization, and smart monitoring systems. IoT sensors and AI-based predictive maintenance will take center stage for ensuring structural integrity and maximizing operational efficiency. These technologies can not only be used to improve the performance of industrial plants but also point the direction towards the future in a sustainable manner.
Industrial Plant Structure Design: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the primary materials used in industrial plant structures?
A: Industrial plant facilities use primarily reinforced concrete, structural steel, and composite materials to be long-lasting and durable.
Q2: How does seismic activity affect industrial plant design?
A: Engineers design structures with seismic-resistant features like flexible joints, shock absorbers, and robust foundations to minimize the effects of earthquakes. Q3: What is the industrial plant design contribution of BIM? A: BIM enables the production of precise 3D models, enhances coordination between the design team, and maximizes project visualization, minimizing errors and rework. Q4: Industrial plants become energy-efficient in which ways? A: With techniques such as using sustainable materials, energy-efficient lighting, and smart HVAC, energy usage in industrial plants can be minimized substantially. Q5: What are typical problems in the design structure of industrial plants? A: Difficulties are supporting heavy weights, giving structural support, following safety regulations, and optimizing the use of space.
Q3: What role does BIM play in industrial plant design?
A: BIM helps create accurate 3D models, improves coordination between design teams, and enhances project visualization, reducing errors and rework.
Q4: How can industrial plants improve energy efficiency?
A: Using sustainable materials, energy-efficient lighting, and smart HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption in industrial plants.
Q5: What are the common challenges in industrial plant structure design?
A: Challenges include managing heavy loads, ensuring structural stability, complying with safety regulations, and optimizing space utilization.
